B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
If a firm's projects differ in risk, then one way of handling this problem is to evaluate each project with the appropriate risk-adjusted discount rate.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
McLeod Inc. is considering an investment that has an expected return of 15% and a standard deviation of 10%. What is the investment's coefficient of variation?
A) 0.67
B) 0.73
C) 0.81
D) 0.89
E) 0.98
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following rules is CORRECT for capital budgeting analysis?
A) Only incremental cash flows, which are the cash flows that would result if a project is accepted, are relevant when making accept/reject decisions.
B) Sunk costs are not included in the annual cash flows, but they must be deducted from the PV of the project's other costs when reaching the accept/reject decision.
C) A proposed project's estimated net income as determined by the firm's accountants, using generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP) , is discounted at the WACC, and if the PV of this income stream exceeds the project's cost, the project should be accepted.
D) If a product is competitive with some of the firm's other products, this fact should be incorporated into the estimate of the relevant cash flows. However, if the new product is complementary to some of the firm's other products, this fact need not be reflected in the analysis.
E) The interest paid on funds borrowed to finance a project must be included in estimates of the project's cash flows.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
We can identify the cash costs and cash inflows to a company that will result from a project. These could be called "direct inflows and outflows," and the net difference is the direct net cash flow. If there are other costs and benefits that do not flow from or to the firm, but to other parties, these are called externalities, and they need not be considered as a part of the capital budgeting analysis.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is NOT a relevant cash flow and thus should not be reflected in the analysis of a capital budgeting project?
A) Shipping and installation costs.
B) Cannibalization effects.
C) Opportunity costs.
D) Sunk costs that have been expensed for tax purposes.
E) Changes in net working capital.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is CORRECT?
A) Only incremental cash flows are relevant in project analysis, the proper incremental cash flows are the reported accounting profits, and thus reported accounting income should be used as the basis for investor and managerial decisions.
B) It is unrealistic to believe that any increases in net working capital required at the start of an expansion project can be recovered at the project's completion. Working capital like inventory is almost always used up in operations. Thus, cash flows associated with working capital should be included only at the start of a project's life.
C) If equipment is expected to be sold for more than its book value at the end of a project's life, this will result in a profit. In this case, despite taxes on the profit, the end-of-project cash flow will be greater than if the asset had been sold at book value, other things held constant.
D) Changes in net working capital refer to changes in current assets and current liabilities, not to changes in long-term assets and liabilities. Therefore, changes in net working capital should not be considered in a capital budgeting analysis.
E) If an asset is sold for less than its book value at the end of a project's life, it will generate a loss for the firm, hence its terminal cash flow will be negative.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Your new employer, Freeman Software, is considering a new project whose data are shown below. The equipment that would be used has a 3-year tax life, and the allowed depreciation rates for such property are 33.33%, 44.45%, 14.81%, and 7.41% for Years 1 through 4. Revenues and other operating costs are expected to be constant over the project's 10-year expected life. What is the Year 1 cash flow? 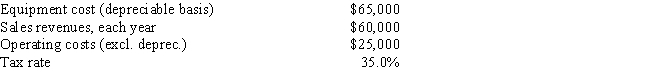
A) $30,333
B) $31,849
C) $33,442
D) $35,114
E) $36,869
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
In cash flow estimation, the existence of externalities should be taken into account if those externalities have any effects on the firm's long-run cash flows.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which one of the following would NOT result in incremental cash flows and thus should NOT be included in the capital budgeting analysis for a new product?
A) A new product will generate new sales, but some of those new sales will be from customers who switch from one of the firm's current products.
B) A firm must obtain new equipment for the project, and $1 million is required for shipping and installing the new machinery.
C) A firm has spent $2 million on R&D associated with a new product. These costs have been expensed for tax purposes, and they cannot be recovered regardless of whether the new project is accepted or rejected.
D) A firm can produce a new product, and the existence of that product will stimulate sales of some of the firm's other products.
E) A firm has a parcel of land that can be used for a new plant site or be sold, rented, or used for agricultural purposes.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Laramie Labs uses a risk-adjustment when evaluating projects of different risk. Its overall (composite) WACC is 10%, which reflects the cost of capital for its average asset. Its assets vary widely in risk, and Laramie evaluates low-risk projects with a risk-adjusted project cost of capital of 8%, average-risk projects at 10%, and high-risk projects at 12%. The company is considering the following projects: Which set of projects would maximize shareholder wealth?
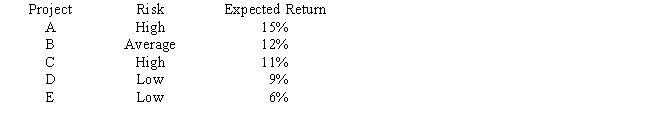
A) A and B.
B) A, B, and C.
C) A, B, and D.
D) A, B, C, and D.
E) A, B, C, D, and E.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The CFO of Cicero Industries plans to calculate a new project's NPV by estimating the relevant cash flows for each year of the project's life (i.e., the initial investment cost, the annual operating cash flows, and the terminal cash flow) , then discounting those cash flows at the company's overall WACC. Which one of the following factors should the CFO be sure to INCLUDE in the cash flows when estimating the relevant cash flows?
A) All sunk costs that have been incurred relating to the project.
B) All interest expenses on debt used to help finance the project.
C) The investment in working capital required to operate the project, even if that investment will be recovered at the end of the project's life.
D) Sunk costs that have been incurred relating to the project, but only if those costs were incurred prior to the current year.
E) Effects of the project on other divisions of the firm, but only if those effects lower the project's own direct cash flows.
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
While developing a new product line, Cook Company spent $3 million two years ago to build a plant for a new product. It then decided not to go forward with the project, so the building is available for sale or for a new product. Cook owns the building free and clear⎯there is no mortgage on it. Which of the following statements is CORRECT?
A) If the building could be sold, then the after-tax proceeds that would be generated by any such sale should be charged as a cost to any new project that would use it.
B) This is an example of an externality, because the very existence of the building affects the cash flows for any new project that Rowell might consider.
C) Since the building was built in the past, its cost is a sunk cost and thus need not be considered when new projects are being evaluated, even if it would be used by those new projects.
D) If there is a mortgage loan on the building, then the interest on that loan would have to be charged to any new project that used the building.
E) Since the building has been paid for, it can be used by another project with no additional cost. Therefore, it should not be reflected in the cash flows for any new project.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Spot-Free Car Wash is considering a new project whose data are shown below. The equipment to be used has a 3-year tax life, would be depreciated on a straight-line basis over the project's 3-year life, and would have a zero salvage value after Year 3. No new working capital would be required. Revenues and other operating costs will be constant over the project's life, and this is just one of the firm's many projects, so any losses on it can be used to offset profits in other units. If the number of cars washed declined by 40% from the expected level, by how much would the project's NPV decline? (Hint: Note that cash flows are constant at the Year 1 level, whatever that level is.) 
A) $28,939
B) $30,462
C) $32,066
D) $33,753
E) $35,530
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Collins Inc. is investigating whether to develop a new product. In evaluating whether to go ahead with the project, which of the following items should NOT be explicitly considered when cash flows are estimated?
A) The project will utilize some equipment the company currently owns but is not now using. A used equipment dealer has offered to buy the equipment.
B) The company has spent and expensed for tax purposes $3 million on research related to the new detergent. These funds cannot be recovered, but the research may benefit other projects that might be proposed in the future.
C) The new product will cut into sales of some of the firm's other products.
D) If the project is accepted, the company must invest $2 million in working capital. However, all of these funds will be recovered at the end of the project's life.
E) The company will produce the new product in a vacant building that was used to produce another product until last year. The building could be sold, leased to another company, or used in the future to produce another of the firm's products.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
VR Corporation has the opportunity to invest in a new project, the details of which are shown below. What is the Year 1 cash flow for the project? 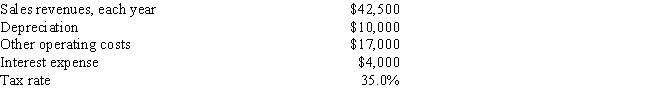
A) $16,351
B) $17,212
C) $18,118
D) $19,071
E) $20,075
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Suppose a firm's CFO thinks that an externality is present in a project, but that it cannot be quantified with any precision⎯estimates of its effect would really just be guesses. In this case, the externality should be ignored⎯i.e., not considered at all⎯because if it were considered it would make the analysis appear more precise than it really is.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Whitestone Products is considering a new project whose data are shown below. The required equipment has a 3-year tax life, and the accelerated rates for such property are 33.33%, 44.45%, 14.81%, and 7.41% for Years 1 through 4. Revenues and other operating costs are expected to be constant over the project's 10-year expected operating life. What is the project's Year 4 cash flow? 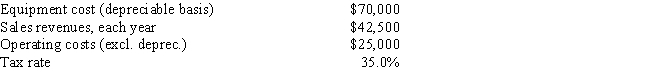
A) $11,904
B) $12,531
C) $13,190
D) $13,850
E) $14,542
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 61 - 78 of 78
Related Exams