B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
As a member of UA Corporation's financial staff, you must estimate the Year 1 cash flow for a proposed project with the following data. What is the Year 1 cash flow? 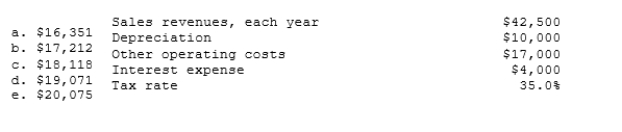
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
If debt is to be used to finance a project, then when cash flows for a project are estimated, interest payments should be included in the analysis.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose Tapley Inc. uses a WACC of 8% for below-average risk projects, 10% for average-risk projects, and 12% for above-average risk projects. Which of the following independent projects should Tapley accept, assuming that the company uses the NPV method when choosing projects?
A) Project A, which has average risk and an IRR = 9%.
B) Project B, which has below-average risk and an IRR = 8.5%.
C) Project C, which has above-average risk and an IRR = 11%.
D) Without information about the projects' NPVs we cannot determine which project(s) should be accepted.
E) All of these projects should be accepted.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
TexMex Food Company is considering a new salsa whose data are shown below. The equipment to be used would be depreciated by the straight- line method over its 3-year life and would have a zero salvage value, and no new working capital would be required. Revenues and other operating costs are expected to be constant over the project's 3-year life. However, this project would compete with other TexMex products and would reduce their pre-tax annual cash flows. What is the project's NPV? (Hint: Cash flows are constant in Years 1-3.) 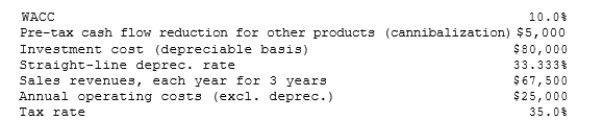
A) $3,636
B) $3,828
C) $4,019
D) $4,220
E) $4,431
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Your company, RMU Inc., is considering a new project whose data are shown below. What is the project's Year 1 cash flow? 
A) $ 8,903
B) $ 9,179
C) $ 9,463
D) $ 9,746
E) $10,039
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Sub-Prime Loan Company is thinking of opening a new office, and the key data are shown below. The company owns the building that would be used, and it could sell it for $100,000 after taxes if it decides not to open the new office. The equipment for the project would be depreciated by the straight-line method over the project's 3-year life, after which it would be worth nothing and thus it would have a zero salvage value. No new working capital would be required, and revenues and other operating costs would be constant over the project's 3-year life. What is the project's NPV? (Hint: Cash flows are constant in Years 1-3.) 
A) $10,521
B) $11,075
C) $11,658
D) $12,271
E) $12,885
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The two cardinal rules that financial analysts should follow to avoid capital budgeting errors are: (1) in the NPV equation, the numerator should use income calculated in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, and (2) all incremental cash flows should be considered when making accept/reject decisions.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Temple Corp. is considering a new project whose data are shown below. The equipment that would be used has a 3-year tax life, would be depreciated by the straight-line method over its 3-year life, and would have a zero salvage value. No new working capital would be required. Revenues and other operating costs are expected to be constant over the project's 3-year life. What is the project's NPV? 
A) $15,740
B) $16,569
C) $17,441
D) $18,359
E) $19,325
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Any cash flows that can be classified as incremental to a particular project--i.e., results directly from the decision to undertake the project--should be reflected in the capital budgeting analysis.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Accelerated depreciation has an advantage for profitable firms in that it moves some cash flows forward, thus increasing their present value. On the other hand, using accelerated depreciation generally lowers the reported current year's profits because of the higher depreciation expenses. However, the reported profits problem can be solved by using different depreciation methods for tax and stockholder reporting purposes.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Aggarwal Enterprises is considering a new project that has a cost of $1,000,000, and the CFO set up the following simple decision tree to show its three most likely scenarios. The firm could arrange with its work force and suppliers to cease operations at the end of Year 1 should it choose to do so, but to obtain this abandonment option, it would have to make a payment to those parties. How much is the option to abandon worth to the firm?

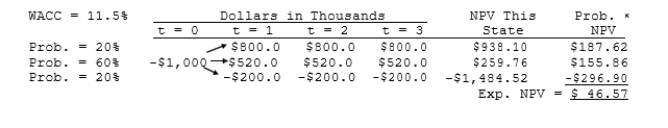
A) $55.08
B) $57.98
C) $61.03
D) $64.08
E) $67.29
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Suppose a firm's CFO thinks that an externality is present in a project, but that it cannot be quantified with any precision--estimates of its effect would really just be guesses. In this case, the externality should be ignored--i.e., not considered at all--because if it were considered it would make the analysis appear more precise than it really is.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is CORRECT?
A) Using accelerated depreciation rather than straight line would normally have no effect on a project's total projected cash flows but it would affect the timing of the cash flows and thus the NPV.
B) Under current laws and regulations, corporations must use straight- line depreciation for all assets whose lives are 5 years or longer.
C) Corporations must use the same depreciation method (e.g., straight line or accelerated) for stockholder reporting and tax purposes.
D) Since depreciation is not a cash expense, it has no effect on cash flows and thus no effect on capital budgeting decisions.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Taussig Technologies is considering two potential projects, X and Y. In assessing the projects' risks, the company estimated the beta of each project versus both the company's other assets and the stock market, and it also conducted thorough scenario and simulation analyses. This research produced the following data:  Correlation of the project cash flows with cash flows from currently existing projects. Cash flows are not correlated with the cash flows from existing projects. Cash flows are highly correlated with the cash flows from existing projects. Which of the following statements is CORRECT?
Correlation of the project cash flows with cash flows from currently existing projects. Cash flows are not correlated with the cash flows from existing projects. Cash flows are highly correlated with the cash flows from existing projects. Which of the following statements is CORRECT?
A) Project X has more stand-alone risk than Project Y.
B) Project X has more corporate (or within-firm) risk than Project Y.
C) Project X has more market risk than Project Y.
D) Project X has the same level of corporate risk as Project Y.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
A firm that bases its capital budgeting decisions on either NPV or IRR will be more likely to accept a given project if it uses accelerated depreciation than if it uses straight-line depreciation, other things being equal.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
You work for Whittenerg Inc., which is considering a new project whose data are shown below. What is the project's Year 1 cash flow? 
A) $25,816
B) $27,175
C) $28,534
D) $29,960
E) $31,458
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Dalrymple Inc. is considering production of a new product. In evaluating whether to go ahead with the project, which of the following items should NOT be explicitly considered when cash flows are estimated?
A) The company will produce the new product in a vacant building that was used to produce another product until last year. The building could be sold, leased to another company, or used in the future to produce another of the firm's products.
B) The project will utilize some equipment the company currently owns but is not now using. A used equipment dealer has offered to buy the equipment.
C) The company has spent and expensed for tax purposes $3 million on research related to the new detergent. These funds cannot be recovered, but the research may benefit other projects that might be proposed in the future.
D) The new product will cut into sales of some of the firm's other products.
E) If the project is accepted, the company must invest $2 million in working capital. However, all of these funds will be recovered at the end of the project's life.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Liberty Services is now at the end of the final year of a project. The equipment originally cost $22,500, of which 75% has been depreciated. The firm can sell the used equipment today for $6,000, and its tax rate is 40%. What is the equipment's after-tax salvage value for use in a capital budgeting analysis? Note that if the equipment's final market value is less than its book value, the firm will receive a tax credit as a result of the sale.
A) $5,558
B) $5,850
C) $6,143
D) $6,450
E) $6,772
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following rules is CORRECT for capital budgeting analysis?
A) The interest paid on funds borrowed to finance a project must be included in estimates of the project's cash flows.
B) Only incremental cash flows, which are the cash flows that would result if a project is accepted, are relevant when making accept/reject decisions.
C) Sunk costs are not included in the annual cash flows, but they must be deducted from the PV of the project's other costs when reaching the accept/reject decision.
D) A proposed project's estimated net income as determined by the firm's accountants, using generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP) , is discounted at the WACC, and if the PV of this income stream exceeds the project's cost, the project should be accepted.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 70
Related Exams